
Business growth necessitates the expansion beyond the boundaries of native markets. With this pace, the demand of perfect translation and localization services is also crucial. Now, the real challenge is not only confined to translate content and data from one language to another but also to refine it according to the cultural and regional expectations. For the guaranteed product services and integrity of brand, the transcription of content and the selection of suitable translation and localization, and making it as per global audience demand is crucial. In this article, the meaningful insights are covered to make proper decision while making the suitable vendor choice for translation and localization services in businesses.
Prior to the selection of a translator or localization provider, it is crucial to comprehend the difference between the two terms. Both the terms are defined as two distinct processes with varied objectives, but often used interchangeably in the business study.
Translation is defined as the transcription of written content from one language to another. The principal purpose is to properly disseminate the basic idea in the target language, while preserving the linguistic credibility.
Localization¸ is an advanced concept, where the purpose is not only to translate the content accurately but also it should be according to the cultural expectations.
It is comprised of cultural practices, rituals, ethical standards, indigenous dialect and cultural rules and custom demands, while protecting integrity of the basic message content and relevancy in the target locale. Localization is significant when acclimating the digital data, marketing contents, product development, or software adaptations for various markets and business sectors.
By understanding these differences, it is crucial to decide whether the proposal demands the primary translation or extensive localization. Investing in localization is the smart plan for firms to attract the customers in a very engaging method in the emerging markets. The difference between translation and localization is depicted in Figure 1.
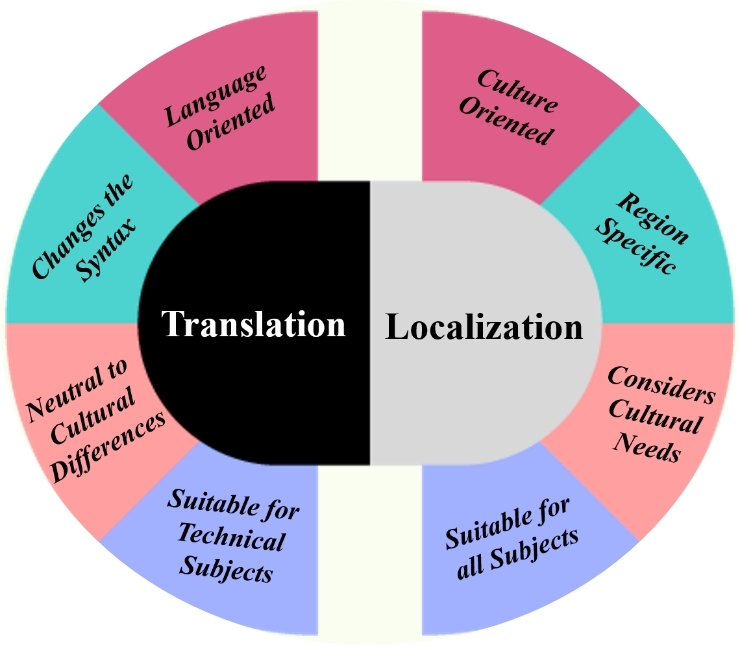
Figure 1: Difference between Translation and Localization
Another major component in the decision making while choosing a translator and localization vendor is their industry experience and proficiency. Translation is not a standard or universal terminology for all services in business. Each business or industry have varied necessities, rules, and terminologies. As for instance, a vendor with proficiency in translating legal files cannot be skillful in translating the documents used in marketing business or information technology. Moreover, the particular experience and knowledge of medical and technical terminologies is mandatory for translating the documents for the healthcare and automobile industries. Along with this the awareness of rules and regulations of the local market is also very important.
For the selection of capable vendors, following qualities should be considered;
Relevant expertise: Does the vendor have the expertise in your desired field? Does he have the knowledge of the terminologies specifically used in your industry?
Former clients: Does he have a working experience of companies, similar to yours in the same region and language pair?
Case studies and references: Can he give case studies or testimonials from companies that are comparable to your company or facing similar challenges?
By choosing a vendor with the suitable experience, one can make sure the precise and correct translation which is appropriate according to the market environment.
The use of native-speaking translators is one of the substantial components to ensure the quality of translation and localization. Language proficiency is crucial, which covers not only basic vocabulary but also align it according to the important cultural ease, unique expressions, social and moral values, which are considered important in that region. The natural and real translation is the craftiness of a native speaker to engage indigenous communities, preventing the unethical phrases and words use, which could be incorporated by a non-native translator.
Further, other than the fluency in language, native-speaking translator can recognize and customize the content, which is not considered suitable in that culture. They are aware of the restrictions, fondness, and the native comicalities to incorporate them in such a way that it should make the content profuse with the moral and social values to align it with the expectations of the target market.
While interviewing a proficient vendor, ask:
Do they employ only native translators for the translation of the required language?
Do the translators have skills in particular area or market?
Do they adapt the cultural values to guarantee the fondness of the local inhabitants?
Native-speaking translators promote the meaningful content which depicts the natural feel and real meaning to the target audience.
In the era of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), each sector requires the proficiency in the technology. The use of technology can play a significant role in the translation and localization processes. The use of translation management systems (TMS), machine translation (MT), and computer-assisted translation (CAT) tools have changed the entire scenario of the businesses, trade and finance markets by avoiding the wastage of time, energy and investment on workforce. The technological tools are of eminent value for the mega projects and their monitoring.
For instance, CAT tools help translators to keep up the database to store the consistent data of multiple projects to harness it for the similar language and the phrases or sentences use for the same market or audience. Similarly, MT is comprised of the tools like Google Translate or others which are specifically designed to accelerate the translation process. However little human efforts are often needed for the final editing to ensure the quality and accuracy.
Regardless of this significance of technology, the human capabilities and expertise should not be neglected. The expert translation and localization providers utilize the combination of both the human translators and the use of technology to get the best results.
For the assessment of vendors, ask:
Are they familiar with the use of advanced tools like TMS or CAT to guarantee the efficacy?
Do they have expertise in machine translation post-editing, especially for projects that need quick repetition of the process?
Do they have customization capabilities to harness the translation tools to your particular requirements or target industry?
A vendor that successfully incorporates technology in their work can act with pace, by saving time and expenditure on translations and maintaining the quality of content.
Localization is a complex process that need a compendious knowledge to commence. It is something more than just translating; is comprised of different components to guarantee the appropriation of the content with the target market. Few important points to keep in control the vendor's localization process are:
Visual and graphic adaptation: Various cultures have different, while designing and selecting, color preferences. A localization vendor must have the knowledge of using and adjusting culturally important images, pictures and icons as per expectations and ethical values.
Technical adaptation: Localization may require technical adaptability while using software or websites to modify and improve the designs ang graphics to align the language that read from right to left (such as Arabic or Hebrew), or those which need more or less space for text.
Legal and regulatory compliancy: Localization may also require the strict control on checking the alignment of content with the local laws and regulations, for example., data privacy laws (such as GDPR in the European Union), local labeling necessity, and industry-specific compliance standards.
A proficient localization supplier will must do a rigorous review of the content to make sure the quality by keeping in mind all the components like language, visual and technical aspects as well as their alignment with the local expectations, social and moral values as per laws and regulations.
Quality assurance (QA) is the fundamental aspect of any perfect translation or localization process. Even in the case of accurate initial translations, keeping checks and controls to maintain the accuracy, stability, and cultural considerations.
A proper QA process primarily requires:
Proofreading and editing: The revision by one or more expert is must to identify and remove the errors and inconsistencies.
Linguistic quality assurance: The accuracy, design and proficiency inspection of the translation to ensure the originality in the target language.
Cultural and contextual review: The revision by cultural experts is also crucial to guarantee the alignment of content with the cultural norms, ethics, customs, and preferences.
Vendors that undergo an extensive process of QA will surely decrease the chance of errors and make sure that the translation will maintain its originality and quality across various languages and markets. Steps involved in quality assurance of a project is shown in Figure 2.
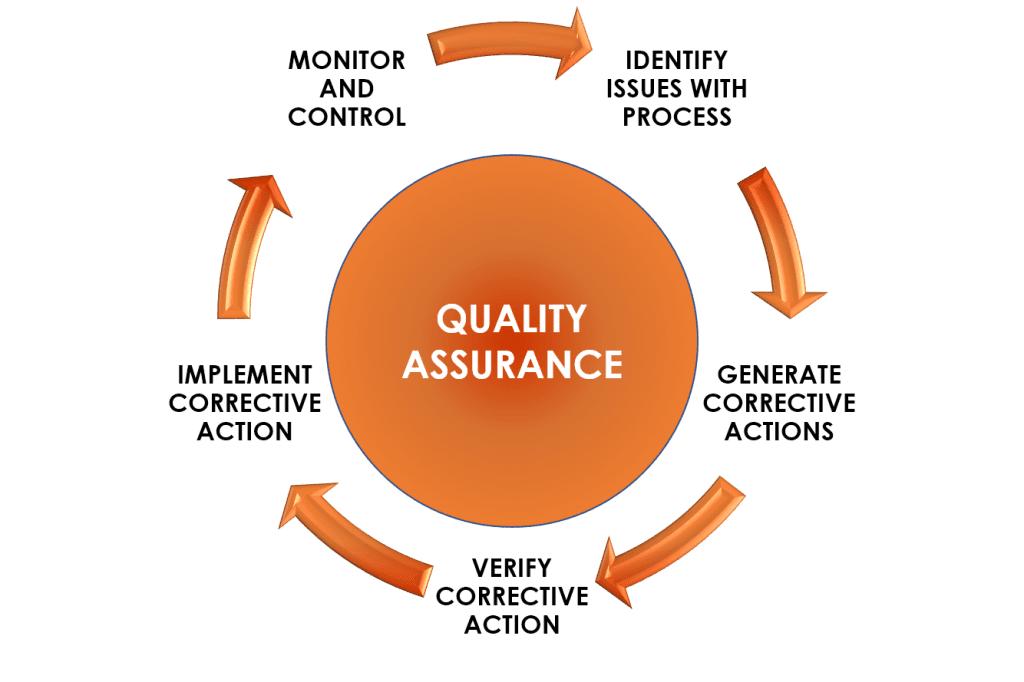
Figure 2: Steps involved in Quality Assurance of a Project
The properly planned project requires an efficient communication and management to ensure that the translation and localization projects must completed on time, within allocated budget, and with high standards. A proficient project manager will keep an eagle eye on each part of the communication chain to address the issues promptly.
For the assessment of potential vendors, ask:
Project timelines: Do they have an experience of keeping track record to successfully complete within the time period, specifically for tight turnaround projects?
Communication: How do they supervise the communication process? Are they active and conscious to response the questions or queries?
Coordination: Do they have coordination experience to effectively connect with your in-house team or other stakeholders working in the project?
An expert project manager who has command on meeting deadlines, keeping strong coordination and communication while understanding the complexities of translation and localization can be effective in maintaining a smooth and efficient process from first step to the last.
Costing is an important aspect in choosing a translation and localization vendor, but it should not be given the primary importance. To select cost effective option is also very essential by keeping the quality control. But the low-quality translations, absence of cultural suitability and norms, and mismanaged communication and missing deadlines can definitely lead to further cost on the business. A higher-priced vendor with a good past record may produce good results.
Quotes obtained from multiple vendors should be compared based on:
The scope of services offered
The expertise of their translators
Their quality assurance processes
By considering value not the cost in this regard can ensure fruitful results in the long term.
Vendors should be assessed with small projects before the large-scale translation and localization project deal closure. This step will help to check their capability and the quality of work overall.
Selecting the potential translation and localization services vendor is a crucial step that notably effect the business ability and to thrive in the global markets. A wisely selected vendor guarantees errorless content which not only meet the criteria of quality like cultural relevance but also boost the brand value and improving connections with global audiences. While finalizing a vendor, aspects such as experience, technological knowledge and proficiency, cost, management and communication skills should be considered carefully to achieve the desired goals. Moreover, identifying project demands, carrying out comprehensive research, requesting multiple quotes, and assessing vendor expertise are crucial steps in the selection process. Negotiation, monitoring and adaptability of vendors should also be considered to ensure profitable and worthwhile collaboration.