In the current scenario, regulations are becoming stricter in the pharmaceutical industry, and ensuring compliance with global regulatory standards is critical for the successful development and approval of new medicines and medical equipment (Janjal et al., 2021). Legislative bodies (like the Food and Drug Administration in the U.S and the European Medicines Agency) that deal with these submissions demand all-inclusive, detailed submissions during the approval process, such as clinical testing safety reports, manufacturing information, and labeling details (Makwana et al., 2021). Though, conventionally these kinds of regulatory submissions have been conducted manually, creating a cause of different issues in terms of precision of the submissions, their management, and efficiency. The development of electronic Common Technical Document (eCTD) has transformed the regulatory submission process to an advanced level, by offering both operational and strategic benefits for pharmaceutical companies (Khristi and Gupta, 2024). Therefore, this article examines the role of eCTD in restructuring regulatory submissions and its impact on ensuring global compliance. Its goal is to motivate pharmaceutical organizations to increase their efficiencies in this area.
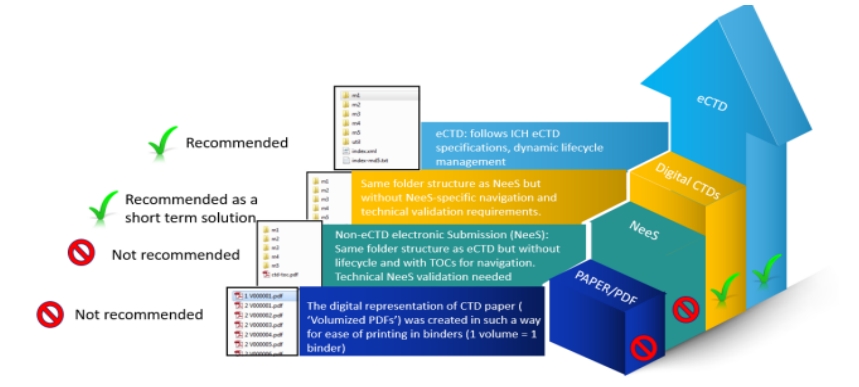
Figure 1 illustrates transitional formats towards eCTD adoption.
eCTD is an internationally recognized format for the submission of regulatory documents in electronic form, which was developed under the guidance of the International Council for Harmonization (ICH), to fulfill the technical requirements (Patil et al., 2024). It provides a unified structure for pharmaceutical companies to submit documents to health-related authorities in a standardized and electronic format. The primary objective of eCTD is to facilitate and simplify the submission process, and the management of these documents in an efficient way. Moreover, eCTD helps ensuring regulatory compliance across different regions. These submissions are organized into structured modules, which include sections such as administrative information, quality data, clinical data, and non-clinical data. This standardization enables both the submitting and regulatory parties to efficiently handle, review, and update these documents in a consistent manner (Essiam, 2024).
Smartness in Submission Processes
Before the development of eCTD, regulatory submissions were primarily based on papers. These often involved too many pages of documentation, exceeding the limit of thousands, and creating handling issues. Thus, pharmaceutical companies faced the frightening task of physically submitting large volumes of paperwork to regulatory bodies which was an unreliable, time consuming, and expensive process (Khristi and Gupta, 2024). The shift to eCTD has eliminated most of its complexity by enabling the submission of documents in an organized electronic format. This smart innovation not only reduces the physical burden on organizations but also ensures reliability, as electronic submissions minimize the risk of missing or misplaced documents.
Quick Approvals
The smart innovation of eCTD has the most important ability which has increased its effectiveness of operational process, and its standardized format through which regulatory affairs team can efficiently manage submission process. In old paper-based system, if there is a need of additional information, the whole data has to be resubmitted but eCTD has a modular update which makes the process smooth. In eCTD, if regulatory body demands for an additional data or interpretation on a specific portion then a company can easily work on specific module without changing the whole submission. This quickness of the process has reduced the risk of time wastage. Thus, if a company required any update in documents of submission process, then it has the facility (Badjatya et al., 2022). Consequently, a medicine company take its products in market quickly which can be an important competitive benefit. Moreover, it is helping in administrative effort, and in result providing the benefit of saving the cost and empowering organizations to allocate different resources more calculatedly.
Improved Tracking and Communication Facility
This smart change facilitates beyond document submissions, and develops communication between pharmaceutical companies and regulatory bodies. Without a doubt, the eCTD publishing platform provides immediate tracking of submissions, and transparency regarding the status of regulatory filings. Both parties, company and regulatory body can monitor progress and identify if any issue raises, and cause the delay in process (Krishna et al., 2023). Additionally, it allows regulatory agencies to issue communications, requests, or updates directly contained by the submission portal. This whole interaction makes it easier for companies to address requests on time, ensuring a faster, more efficient regulatory review process. This digital communication reduces delays in processes and improves overall collaboration, leading to better outcomes for both the pharmaceutical company and the regulatory bodies.
Better Management of the Multiple Versions through eCTD
Another benefit with the implementation of eCTD is its inherent version control system. Managing multiple versions of documents has previously been a challenge, especially with paper-based filings where tracking changes was inconvenient (Sudesamithiran, 2023). But with this smart innovation, systems automatically maintain a complete version history for each document, ensuring a clear audit trail of all modifications made during the submission process. Moreover, this version management system is really important for regulatory agencies, as it makes sure they always have access to the most updated documentation. It also reduces the risk of submitting invalid or incomplete data, which can delay approval or lead to penalties from regulatory bodies. The system’s transparency and traceability make this smart innovation a key tool for maintaining the integrity of regulatory submissions (Makwana et al., 2021).
Global Harmonization of Regulatory Standards
The start of eCTD has been a significant step for upgrading, and harmonizing regulatory submission processes through various authorities. Bodies that are involved in making legislations have given the preference to eCTD. These worldwide arrangements of regulations, facilitates pharmaceutical companies to submit a single eCTD report that meets the standards of various regulatory bodies at the same time, and help in removing the requirement to create separate submissions for different regions. Additionally, this harmonization is considerable for operational efficiencies of the firms, and they have no longer need to prepare and submit multiple versions of the same document in different formats for each regulatory body in different regions. Instead of this, a single eCTD submission can be personalized to meet the requirements of multiple health authorities (Huma and Peng, 2023). Consequently, it has a strong impact on reducing administrative cost in the firms, and the risk of noncompliance with regulatory bodies.
Compliance with Regulatory Upgradations
Implementation of eCTD enables pharmaceutical companies to stay active in the face of rapidly upgrading policies. As global arrangements required comprehensive policies, regulatory bodies making changes in their policies day by day to upgrade the standards, pharmaceutical companies can quickly adapt their eCTD submissions to reflect the most current standards. The flexible structure of eCTD allows companies to make changes to specific sections without disturbing the reliability and accuracy of the complete submission document (Rupnawar and Wani, 2024). Whether it is an update related to some medical data or a modification to manufacturing details, companies can respond easily to new policies, and can make compliance with the latest standards that are set by the regulatory bodies.
Reducing Risk and Ensuring Compliance
By merging all regulatory documents in a single and systematized repository, eCTD helps pharmaceutical companies to minimize the risks of mistakes, such as some missing documents, or delays in submission deadlines. Moreover, keeping a view on global issues regulatory bodies are increasingly demanding greater standards of compliance (Patil et al., 2024). Otherwise, small mistakes or omissions can lead to expensive delays or rejections in the submissions. Moreover, with the help of this innovation, centralized document management system allows regulatory affairs teams to manage visibility of all submission materials. Likewise, immediate updates, version control, and automated tracking ensure that nothing falls through the cracks. This all-inclusive management reduces the risk of noncompliance and enhances the company’s ability to meet regulatory deadlines without costly mistakes.
Faster Entry in the Market
The implementation of eCTD not only provides the benefits of operational efficiencies but also offers strategic advantages in the market. Because, speeding up the submission and approval process, supports pharmaceutical companies to bring their products in market faster, and before the competitors do. The ability to quickly respond to regulatory queries and resubmit updated information in an efficient way can make a significant difference in the global competitive environment in pharmaceutical industry (Rupnawar and Wani, 2024). Furthermore, as regulatory bodies continue to embrace eCTD as the global standard, companies that adopt this phenomenal innovation early gain a competitive edge, and with the help of which they can avoid the delays and control different expenses associated with it.
Reducing Complexity and Harmonized Submissions
The eCTD offers a modernized approach for multinational pharmaceutical companies in regulatory submissions across different countries. Instead of initiating multiple submissions, a company can adapt a single and harmonized submission by reducing the complexity of global compliance that can be accepted by multiple regulatory bodies (Sudesamithiran, 2023). This smart innovation ensures that all regulatory requirements are met in a consistent manner, allowing companies to focus on their core activities like medicines development and innovation in equipment without being trapped by the complexities of different regulatory systems in different regions.
Reducing Risks and Maintaining Visibility
The risk of neglecting or inadequate submissions is a significant concern in the industry like pharma where rules and regulations are very strict. In case of missing documents, incorrect versions, or outdated data can lead to delays, fines, or even rejection by regulatory bodies (Khristi and Gupta, 2024). Therefore, eCTD is the best solution for centralizing all regulatory documents in one system. It also reduces the risk of errors and omissions that can derail the approval process. Moreover, the version control system inherent in eCTD capable of ensuring that only the most current and accurate documents are submitted to regulatory bodies, minimizing the risk of incorrect data being reviewed. Likewise, the ability to track every change made to a document provides a clear audit trail, enabling companies to maintain full visibility on the submission process and ensuring compliance at every stage of the process.

Figure 2 illustrates a snapshot of key strategies for the future of regulatory submissions.
The smart innovation of eCTD represents a model shift by means of pharmaceutical companies manage regulatory submissions. Its ability to smart submission processes, improve efficiency, and ensure global compliance has transformed the regulatory management to an advanced level. As regulatory bodies around the world continue to adopt eCTD as the basic standard, its importance will only grow. Moreover, from the pharmaceutical companies’ perspective, utilizing eCTD platform is not just a technological upgradation, but it is a strategic decision that initiates faster market entry, lowers operational costs, and improves global competitiveness. In a highly regulated and competitive environment where rules are really strict, acquiring eCTD offers pharmaceutical companies a clear path toward greater operational efficiency and improved regulatory compliance.
Badjatya, J. K., Jangid, A., Dodiya, P., Soni, S., Parekh, A., Patel, D., & Patel, J. (2022). Comparative study of Regulatory requirements of Drug Product in Emerging market. International Journal Of Drug Regulatory Affairs, 10(1), 51-82.
Essiam, I. (2024). Regulatory convergence or harmonisation? Exploring regional approaches for streamlining chemistry manufacturing and control variations and its application in Latin America compared to initiatives in Southeast Asia (Doctoral dissertation, Cardiff University).
Huma, T., & Peng, Z. (2023). Introduction to Regulatory Affairs and Different Regulatory Bodies for Pharmaceutical Products and Impact of Digitalization on Regulatory Affairs. Pharmacology & Pharmacy, 14(11), 463-477.
Janjal, V. S., Dhamodkar, S. R., Jadhao, Y. P., Manmode, S. B., Pawar, A. K., & Khandelwal, H. R. (2021). Recent drug regulatory affair and CTD module progress review for submission of pharmaceuticals product. GSC Biological and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 16(3), 200-221.
Khristi, A. P., & Gupta, V. (2024). Regulatory Approval and Challenges in the Digital Era. In Converging Pharmacy Science and Engineering in Computational Drug Discovery (pp. 270-286). IGI Global.
Krishna, P. V. S., Babu, P. S., Rao, C. V. P., Keerthi, M., Kousalya, O., Reddy, A. M., ... & Manikanta, T. S. (2023). Navigating Regulatory Landscapes: A Comprehensive Exploration of New Drug Approval Dossiers in the Complex Markets of the US, EU, and India. Journal for ReAttach Therapy and Developmental Diversities, 6(1), 834-941.
Makwana, R. G., Desai, K. V., Kikani, V., & Vaja, M. D. (2021). Regulatory advances and prospects of variation filing for the registered parenteral products in USA and Europe. International Journal Of Drug Regulatory Affairs, 9(2), 52-65.
Patil, N. S., Ranjan, A., Narang, R. K., & Singh, A. (2024). Evaluating the Imperative Role of Pre-and Post-eCTD Standards in Dossier Validation: An Inevitable Outlook. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 30(18), 1379-1381.
Rupnawar, M., & Wani, P. (2024). Pharmaceutical Regulatory Affairs: An Overview of Global Regulatory Frameworks and Emerging Trends. Int. J. Sci. R. Tech, 1(12).
Sudesamithiran, N. (2023). A review on next generation eCTD-eCTD v4. 0. International Journal Of Drug Regulatory Affairs, 11(4), 67-73.